As the nation’s housing stock continues to age and new homes remain out of reach for many buyers, remodeling is capturing a growing share of the residential construction market, both in terms of the number of firms and employment. With most U.S. households unable to afford new construction, renovation has become a more practical and cost-effective alternative to improve housing conditions, driving demand on the consumer side. On the supply side, many home builders undertake remodeling projects to grow their business. NAHB’s analysis of the quarter-century of Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages (QCEW) data suggests that the rise of remodelers is a sustained structural shift rather than a temporary post-pandemic surge.
Remodeling Firms’ Share in Residential Construction is Rising
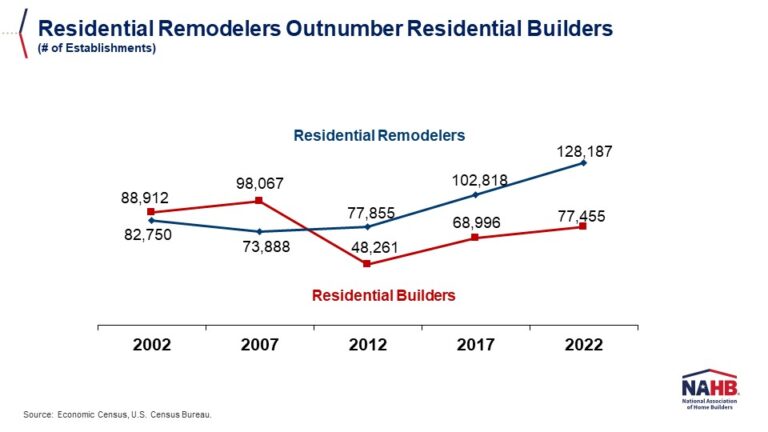
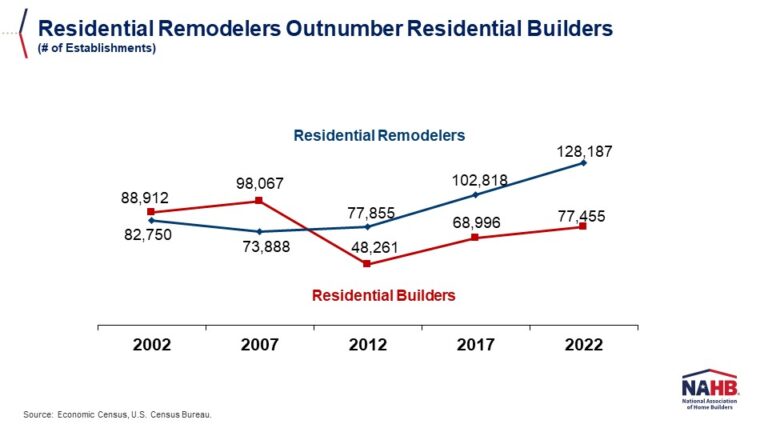
Over the past 25 years, the number of remodeling establishments has nearly doubled—from fewer than 69,000 in 2000 to more than 128,000 in the first quarter of 2025. Remodelers now represent over half (56%) of all residential building construction (RBC) establishments. By contrast, during the mid-2000s housing boom, remodelers’ share consistently hovered around 38–39%, when the market was dominated by home builders, including new single-family and multifamily general contractors as well as speculative (spec) home builders.
Although the remodeling sector was not immune to the 2008 housing crash, its losses were modest compared to the contraction of home building. Between 2007 and 2012, the number of remodeling establishments fell by 8%, while roughly one-third of home builders went out of business. As a result, the remodeler’s share of the RBC sector rose sharply after the crash, reaching 46% in 2011, and has continued to climb steadily ever since.
During the post-pandemic housing boom, driven by low mortgage rates, the rise of remote work, and a renewed demand for larger living spaces, both remodelers and home builders experienced solid growth. However, remodelers expanded their ranks at a faster pace, with their share of RBC firms climbing to 54% by 2022. Less sensitive to fluctuations in mortgage rates than home builders, remodelers have continued to grow even amid a series of aggressive Federal Reserve rate hikes that sharply increased the cost of home purchases and slowed new construction. As of 2024, remodeling firms account for 56% of all RBC establishments.
Remodeling Employment Share in RBC is Rising
In the overall construction industry, which encompasses residential and non-residential building construction, as well as heavy/civil engineering construction, land subdivision, and specialty trade contractors, it is the latter that dominate the overall sector employment. However, the government employment surveys cannot identify what portion of subcontractors’ business is devoted to remodeling. As a result, RBC is the subsector that allows tracking the remodeling trends best.
The analysis of employment trends in residential building construction reveals a similar pattern, with remodelers generating a rising number and share of jobs, largely at the expense of single-family general contractors. As of 2024, the remodeling sector accounted for almost half (49%) of RBC workers. In contrast, during the housing boom of the mid-2000s, only 30% of payroll employees worked for remodelers, while single-family general contractors employed 63% of the RBC workforce.
The shift is even more pronounced within the production (nonsupervisory) workforce of the RBC industry. More than half (51.2%) of these skilled craftsmen now work for remodeling firms, compared with roughly 30% in the early 2000s, according to NAHB’s analysis of historical data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ Current Employment Statistics (CES) survey.
Multifamily general contractors, who subcontract out most of their construction work, account for a smaller share of home building jobs but have also gained ground. Fueled by strong multifamily activity in 2022–2023, their share of RBC employment grew to 5% by 2024. For-sale builders account for an additional 6%.
The typical remodeling firm remains small, averaging between 3 and 4 employees per establishment, comparable to levels observed during the mid-2000s housing boom. This stability suggests that the overall rise in remodeling employment stems primarily from the creation of new firms or the reclassification of home builders shifting toward renovation work as remodelers. It is likely that, as market conditions change, some home builders, particularly smaller single-family general contractors, pivot toward renovation projects to stay and grow their business. The remodeling sector’s lower barriers to entry, smaller upfront investments compared to new construction, and fewer regulatory hurdles make the transition easier.
As more companies view remodeling as their primary activity and revenue source, more will be reclassified as remodeling establishments in the official data reporting. This is because data collection in the U.S. is guided by the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). Under NAICS, a company self-classifies and chooses the industry code that best captures its primary activity. In some surveys, such as the Economic Census, the Census Bureau emphasizes revenue sources as a primary metric for categorizing businesses. The steadily rising number of remodelers and the jobs they create underscores that renovation has become the reliable engine driving growth in the residential construction sector.