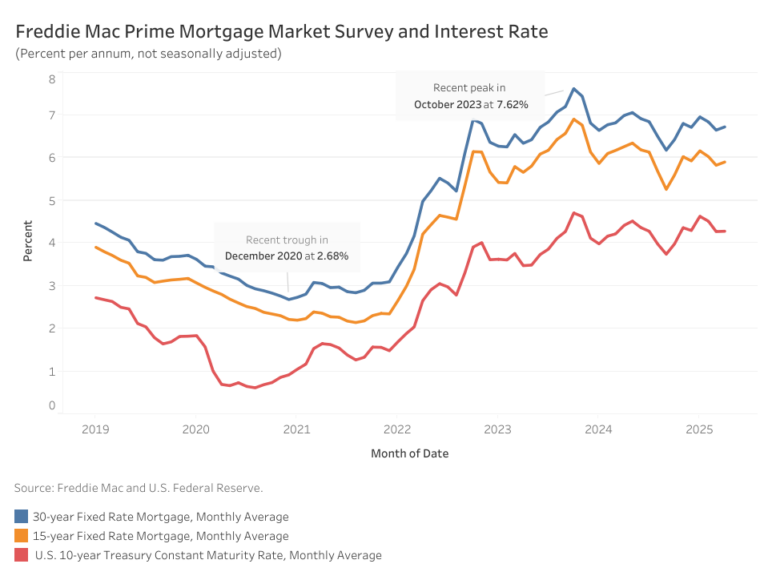
As housing affordability remains a critical challenge across the country, mortgage rates continue to play a central role in shaping homebuying power. Mortgage rates stayed elevated throughout 2023 and early 2024. Recent data, however, shows a modest decline in mortgage rates. Even slight declines can have a significant impact on housing affordability, pricing more households back into the market. New NAHB Priced-Out Estimates show how home price increases affect housing affordability in 2025. This post presents details regarding how interest rates affect the number of households that can afford a median priced new home.
At the beginning of 2025, with the average 30-year fixed mortgage rate at 7%, around 31.5 million households could afford a median-priced home at $459,826. This requires a household income of $147,433 by the front-end underwriting standards[1]. In contrast, if the average mortgage rates had remained at the recent peak of 7.62% in October 2023, only 28.7 million households would have qualified. This 62-basis point decline has effectively priced 2.8 million additional households into the market, expanding homeownership opportunities.
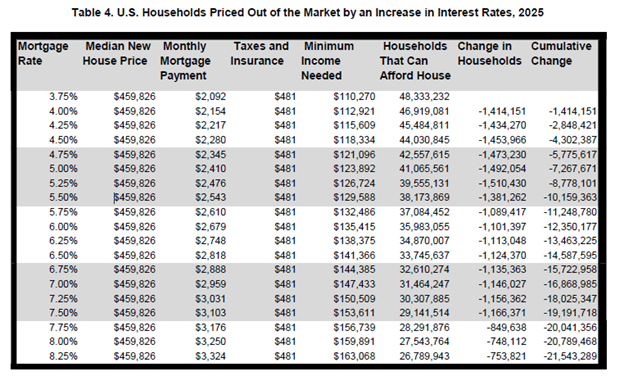
The table below shows how affordability changes with each 25 basis-point increase in interest rates, from 3.75% to 8.25% for a median-priced home at $459,826. The minimum required income with a 3.75% mortgage rate is $110,270. In contrast, a mortgage rate of 8.25%, increases the required income to $163,068, pushing millions of households out of the market.
As rates climb higher, the priced-out effect diminishes. When interest rates increase from 6.5% to 6.75%, around 1.13 million households are priced out of the market, unable to meet the higher income threshold required to afford the increased monthly payments. However, an increase from 7.75% to 8% would squeeze about 850,000 households out of the market.
This exemplifies that when interest rates are relatively low, a 25 basis-point increase has a much larger impact. It is because it affects a broader portion of households in the middle of the income distribution. For example, if the mortgage interest rate decreases from 5.25% to 5%, around 1.5 million more households will qualify the mortgage for the new homes at the median price of $459,826. This indicates lower interest rates can unlock homeownership opportunities for a substantial number of households.
[1] . The sum of monthly payment, including the principal amount, loan interest, property tax, homeowners’ property and private mortgage insurance premiums (PITI), is no more than 28 percent of monthly gross household income.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.