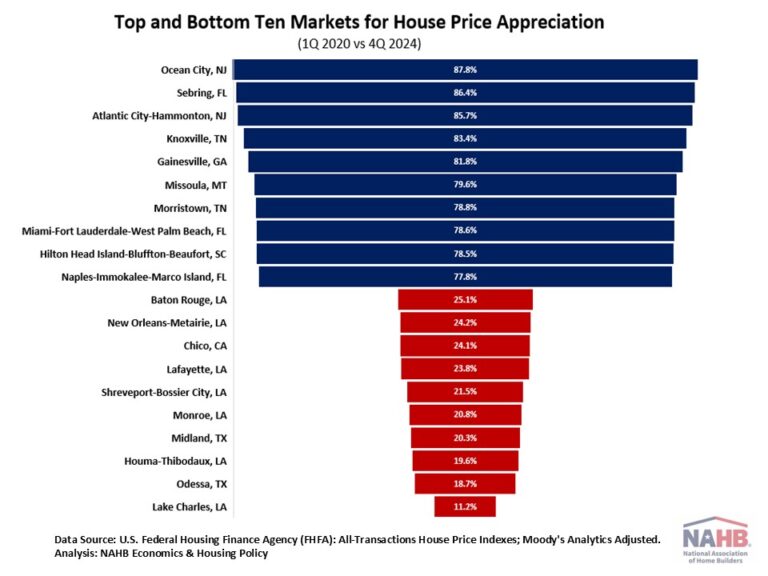
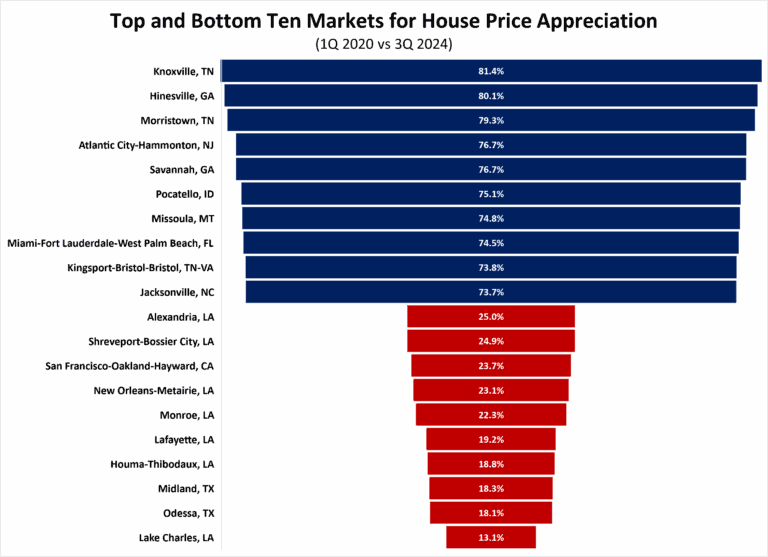
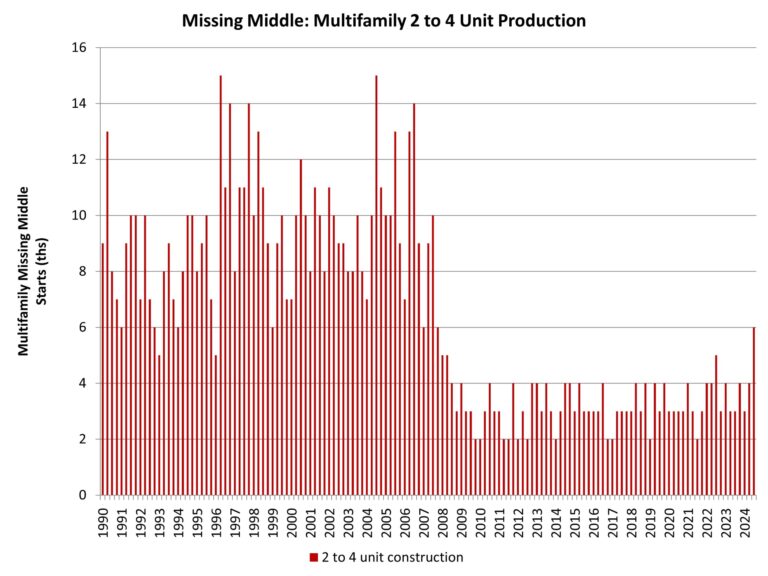
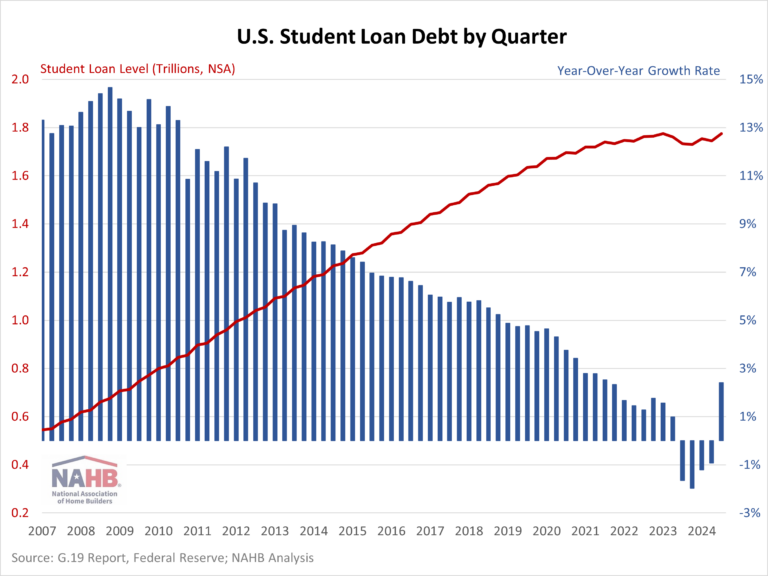
Sentiment declined among remodelers in the first quarter of 2025, following a similar trend last month in single-family home builder sentiment. The NAHB/Westlake Royal Remodeling Market Index (RMI) posted a reading of 63 in the first quarter, down five points compared to the previous quarter. While this reading is still in positive territory, this is only the second time since the first quarter of 2020 that the RMI has been as low as 63.
Tariffs and economic uncertainty were top-of-mind for consumers this quarter. Although almost all the data for the first quarter RMI were collected before the release of specific reciprocal tariffs, the debate and uncertainty over tariffs has had an effect on consumer confidence. Moreover, remodelers responding to the special questions as part of the RMI survey reported that their suppliers have already increased prices by an average of 6.9% since January 20, due to the anticipated effect of tariffs.
Nevertheless, strong tailwind factors, such as an aging population, aging housing stock, home equity gains post-COVID, and “locked-in” (definition) existing homeowners, will continue to keep remodeling spending solid for the foreseeable future according to NAHB’s forecast.
The RMI is based on a survey that asks remodelers to rate various aspects of the residential remodeling market “good”, “fair” or “poor.” Responses from each question are converted to an index that lies on a scale from 0 to 100. An index number above 50 indicates a higher proportion of respondents view conditions as good rather than poor.
Current Conditions
The Remodeling Market Index (RMI) is an average of two major component indices: the Current Conditions Index and the Future Indicators Index.
The Current Conditions Index is an average of three subcomponents: the current market for large remodeling projects ($50,000 or more), moderately sized projects ($20,000 to $49,999), and small projects (under $20,000). In the first quarter of 2025, the Current Conditions Index averaged 71, dropping four points from the previous quarter. While the component measuring small-sized projects remained unchanged at 76, moderately-sized remodeling projects inched down one point to 72 and large remodeling projects fell 11 points to 64. However, all three components remained above 50 in positive territory.
Future Indicators
The Future Indicators Index is an average of two subcomponents: the current rate at which leads and inquiries are coming in, and the current backlog of remodeling projects.
In the first quarter of 2025, the Future Indicators Index averaged 55, down six points from the previous quarter. Both subcomponents experienced decreases quarter-over-quarter, with the component measuring the backlog of remodeling jobs inched down one point to 58 and the component measuring the current rate at which leads and inquiries are coming in fell 11 points to 51.
For the full set of RMI tables, including regional indices and a complete history for each RMI component, please visit NAHB’s RMI web page.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .