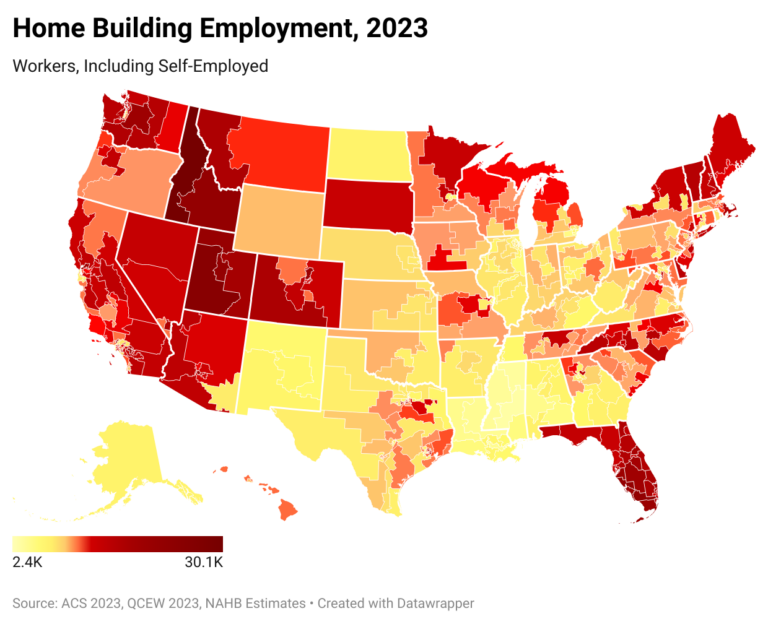
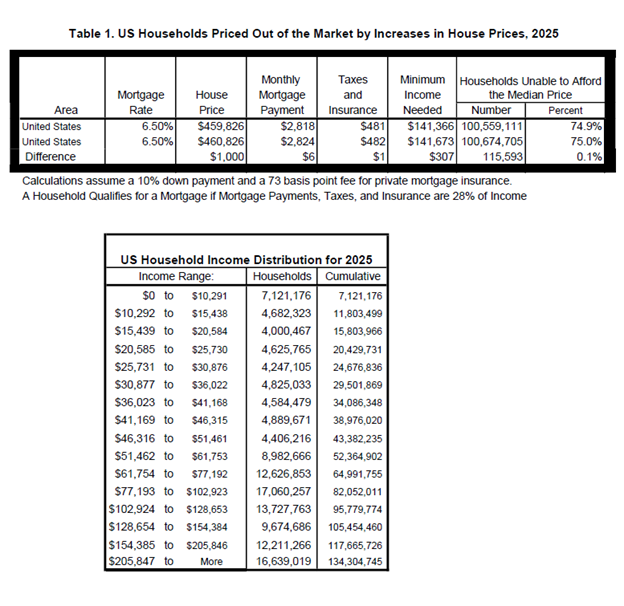
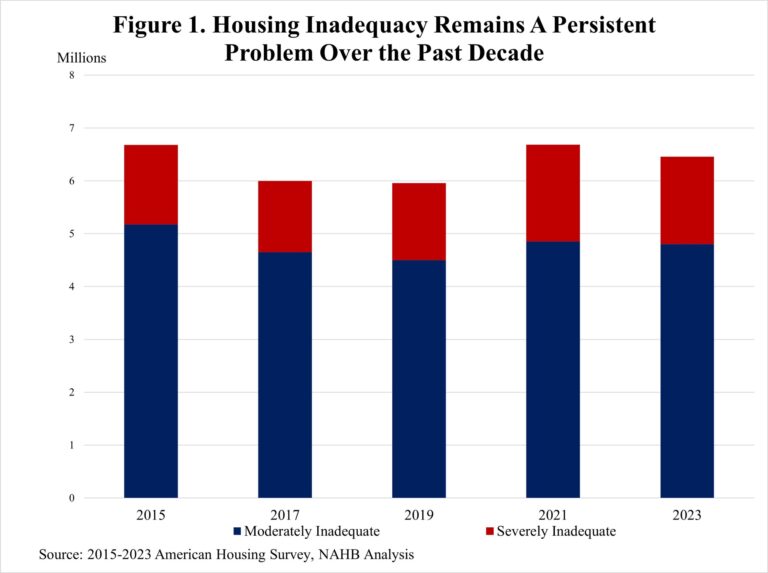
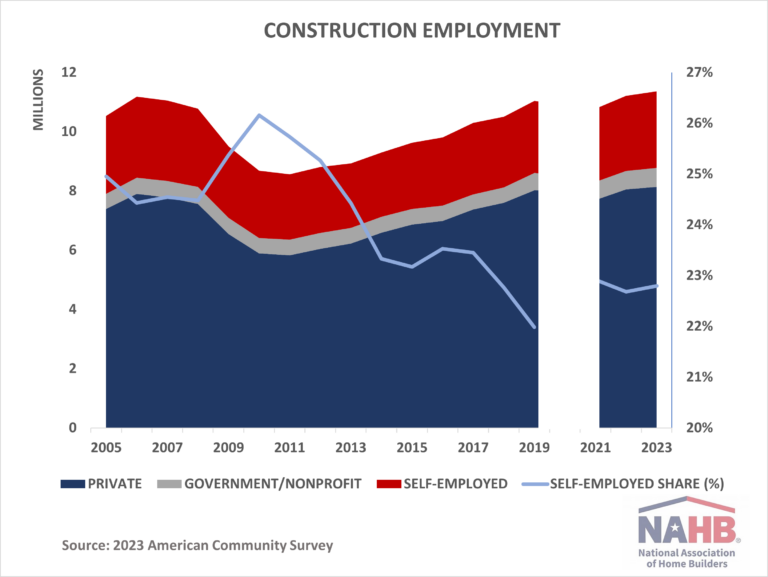
Home builders have already started to feel the effects of U.S. tariff policy, according to recent NAHB member surveys. This is true even though the Administration did not announce its list of reciprocal tariffs until April 2nd, lumber along with USMCA-compliant imports from Canada and Mexico were exempt, and a week later the Administration enacted a 90-day hiatus, with tariffs on countries other China limited to 10% over this time. The Administration subsequently granted further temporary exemptions from the reciprocal tariffs for a broad range of electronic products imported from China.
After all this, significant uncertainty about the final outcome still remains. The U.S. may revisit trade policy for Canada and Mexico, China-U.S. negotiations are unsettled, and the effects of the 10% tariff on building products from other countries are difficult to predict. Moreover, exactly what will happen at the end of the 90-day hiatus is unclear. In the meantime, economic uncertainty can adversely affect consumer confidence and make prospective home buyers hesitate. This is one of the reasons the NAHB/Wells Fargo Housing Market Index (HMI) declined in March.
The latest NAHB estimate (based on cost data from RSMeans and PPI inflation rates) is that the average new single-family home requires $174,155 worth of building materials. Previous NAHB research has shown that 7.3% of materials in residential construction, or $12,713 of materials costs for the average single-family home, is imported.
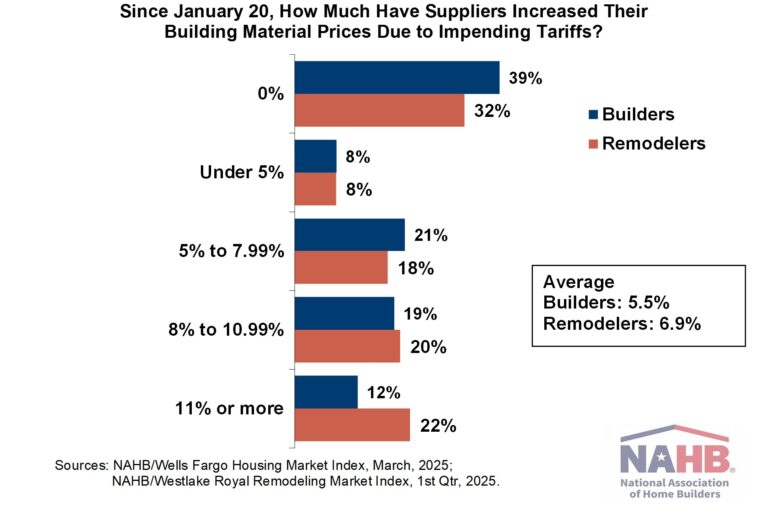
Based on this, it may seem that tariffs would have a limited effect on home builders. However, as noted above, the uncertainty caused by the mere announcement of tariffs can have an adverse effect on the behavior of consumers and even businesses. In recent surveys, NAHB builders and remodelers reported that building material suppliers had already increased their prices—by an average of 5.5% and 6.9%, respectively—due to announced, enacted or anticipated tariffs.
The data on builders came from the HMI survey and were collected during the first two weeks of March. The data on remodelers came from the survey for the NAHB/Westlake Royal Remodeling Market Index and were collected during the last week of March and first three days of April.
NAHB will continue to monitor material prices given the uncertainty and fluidity of the tariff situation.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .