In the latest 2023 NAHB member census, 21% of NAHB builder members listed residential remodeling as their primary business. These remodelers tend to be relatively small, with a median of five employees and a median annual revenue of $1.8 million. They are thus even smaller than NAHB builder members in general, who had a median of six employees and median annual revenue of $3.4 million, as reported in a recent post.
Among the residential remodelers, 21% reported a dollar volume of less than $500,000 in 2023, 20% reported between $500,000 and $999,999, 47% between $1.0 and $4.9 million, 8% between $5.0 and $9.9 million, 2% between $10.0 million and $14.9 million, and another 2% reported $15.0 million or more. None reported zero business activity in 2023.
The median annual revenue for residential remodelers in 2023 was $1.8 million—considerably below the $3.4 million median calculated across all NAHB builder members, and a small fraction of the $45.0 million threshold the Small Business Administration uses to classify construction businesses as small. Even so, residential remodelers’ median revenue was up from the $1.2 million recorded in 2022.
The median number of payroll employees was also relatively small among NAHB’s residential remodelers in 2023—five, compared to six for all NAHB builder members. Both numbers were unchanged from 2022.
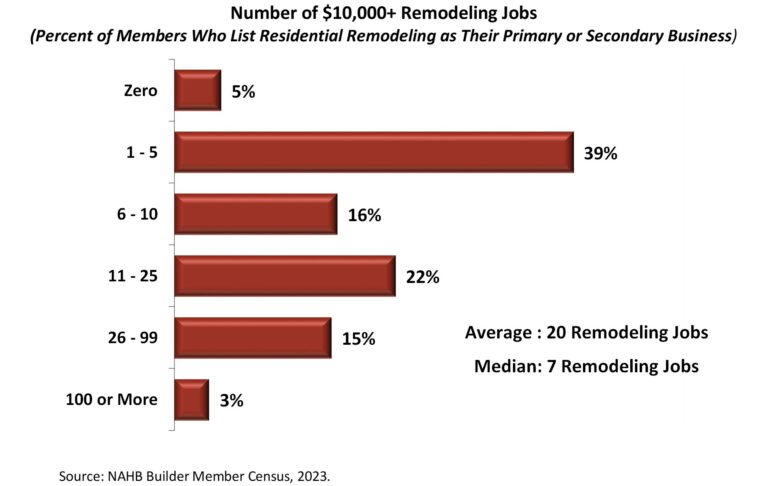
To provide a measure of housing activity roughly analogous to starts, the NAHB census asked builder members who are primarily or secondarily residential remodelers about the number of remodeling jobs they completed in 2023 costing $10,000 or more. The responses show that a plurality of 39% completed 1 to 5 jobs of this size, 16% did 6 to 10, 22% did 11 to 25, 15% did 26 to 99, and 3% completed 100 or more jobs costing more than $10,000. On average, builder members involved in residential remodeling as a primary or secondary activity completed 20 jobs costing $10,000 or more in 2023. The median number was 7.
The numbers are significantly higher if the calculations are confined to the 21% of NAHB builder members who list residential remodeling specifically as their primary activity. These members completed an average of 32 and a median of 15 $10,000-plus jobs in 2023. These results are not significantly different from the ones reported in 2022, when NAHB first included the remodeling jobs question in its member census.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .