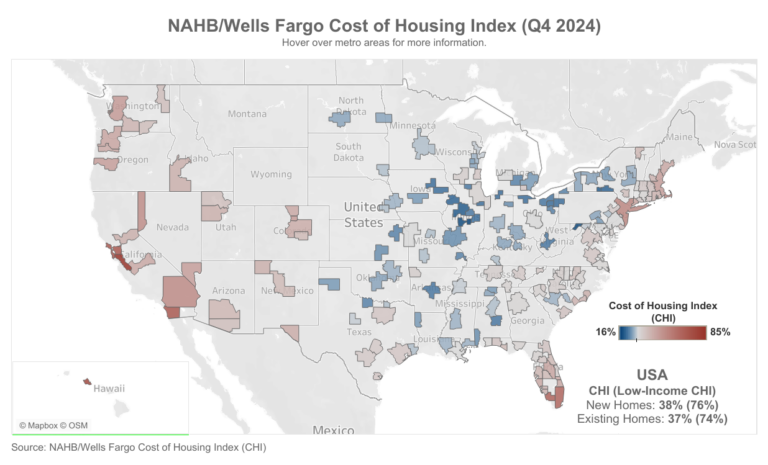
In a clear sign illustrating the housing affordability challenges facing Americans, the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB)/Wells Fargo Cost of Housing Index (CHI) found that in the fourth quarter of 2024, a family earning the nation’s median income of $97,800 needed 38% of its income to cover the mortgage payment on a median-priced new home. Low-income families, defined as those earning only 50% of the median income, would have to spend 76% of their earnings to pay for the same new home.
The figures track closely for the purchase of existing homes in the U.S. as well. A typical family would have to pay 37% of their income for a median-priced existing home, while a low-income family would need to pay 74% of their earnings to make the same mortgage payment.
There was no change in the percentage of a family’s income needed to purchase a new home (38%) between the third and fourth quarters of 2024. However, the cost burden did increase slightly for low-income families, rising from 75% to 76% of their income.
Meanwhile, the cost burden of existing homes edged lower for both median- and low-income families between the third and fourth quarter. The CHI indices were 37% and 74%, respectively, in the fourth quarter, down from 38% and 75% in the third quarter. The slight uptick in affordability was due to median existing home prices falling 2% from the third quarter to the fourth quarter of 2024.
CHI is also available for 176 metropolitan areas, calculating the percentage of a family’s income needed to make the mortgage payment on an existing home based on the local median home price and median income in those markets.
In 10 out of 176 markets in the fourth quarter, the typical family is severely cost-burdened (must pay more than 50% of their income on a median-priced existing home). In 85 other markets, such families are cost-burdened (need to pay between 31% and 50%). There are 81 markets where the CHI is 30% of earnings or lower.
The Top 5 Severely Cost-Burdened Markets
San Jose-Sunnyvale-Santa Clara, Calif., was the most severely cost-burdened market on the CHI, where 87% of a typical family’s income is needed to make a mortgage payment on an existing home. This was followed by:
Urban Honolulu, Hawaii (74%)
San Diego-Chula Vista-Carlsbad, Calif. (69%)
San Francisco-Oakland-Berkeley, Calif. (69%)
Naples-Marco Island, Fla. (65%)
Low-income families would have to pay between 129% and 174% of their income in all five of the above markets to cover a mortgage.
The Top 5 Least Cost-Burdened Markets
By contrast, Decatur, Ill., was the least cost-burdened market in the CHI, where typical families needed to spend just 16% of their income to pay for a mortgage on an existing home. Rounding out the least burdened markets are:
Cumberland, Md.-W.Va (17%)
Springfield, Ill. (17%)
Elmira, N.Y. (19%)
Peoria, Ill. (19%)
Low-income families in these markets would have to pay between 31% and 39% of their income to cover the mortgage payment for a median-priced existing home.
Visit nahb.org/chi for tables and details.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.