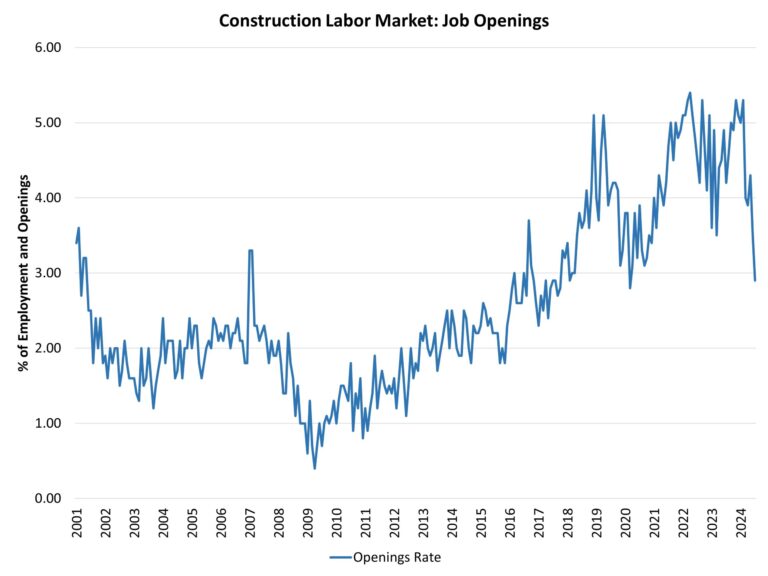
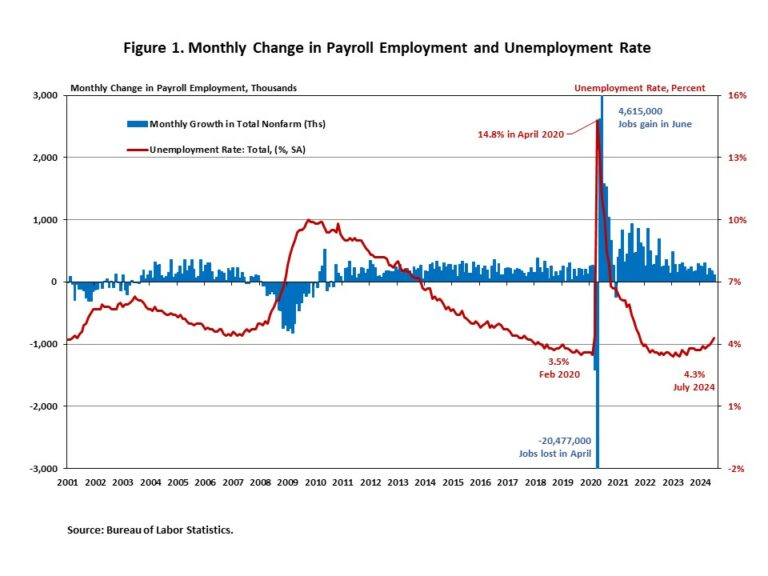
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), people who are neither working nor looking for work are counted as “not in the labor force”. Understanding the size and characteristics of individuals not in the labor force is crucial for a comprehensive assessment of the job market and overall economic health, as it provides insights into potential labor supply and demand issues.
Size
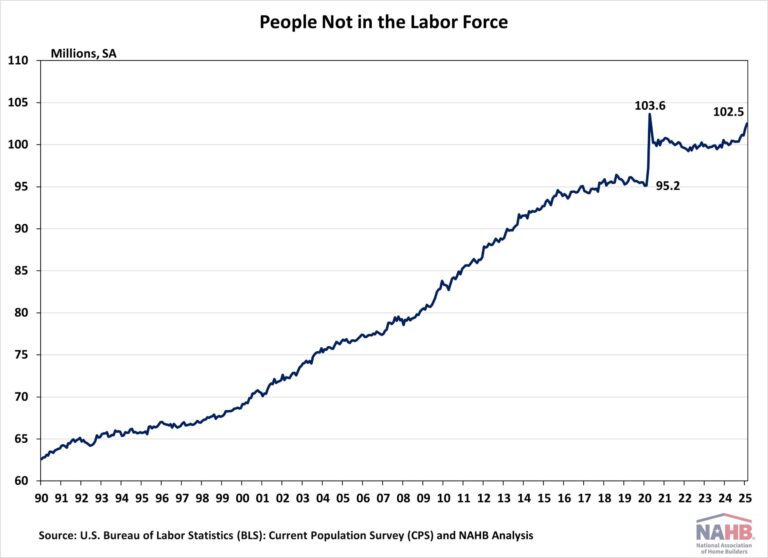
The number of people not in the labor force has been steadily increasing. As of February 2025, data from the BLS indicates that 102.5 million people, aged 16 or older, were not in the labor force. During the COVID-19 pandemic, this figure surged sharply, rising from 95.2 million in February 2020 to a historically high 103.6 million in April 2020. Since then, the number has remained around 100 million, with a noticeable upward trend over the past year.
Characteristics
Data from the 2024 Current Population Survey (CPS) and the Annual Social and Economic Supplement (ASEC) offer valuable insights into why individuals are not in the labor force. The ASEC gathers information on employment and unemployment experienced during the previous calendar year. The data used in this article focus on individuals aged 16 years and older who neither worked nor looked for a job in 2023.
According to the analysis of the data from the 2024 CPS and ASEC, approximately 93.6 million people aged 16 or older were not in the labor force in 2023. Among this group, nearly 39 million (42%) were men, and 54.6 million (58%) were women.
In terms of age distribution, about 49% of those not in the labor force were aged 65 years or older. Additionally, 13% were between the ages of 55 and 64, 21% were between the ages of 25 and 54, and the remaining 17% were aged 24 or younger. Intuitively, people aged 65 years and older represented the largest share of individuals who were not in the labor force.
Regarding educational attainment, 51% of individuals not in the labor force had a high school diploma or lower. Those with some college education made up 24%, while individuals with a bachelor’s degree or higher accounted for 25%.
The racial breakdown of those not in the labor force is as follows: 58.2 million were non-Hispanic white, 15.4 million were Hispanic, 11.7 million were Black, 5.9 million were Asian, and the remaining 2.5 million identified as other races.
Main Reason for Not Working
The group of people not in the labor force is diverse, and the reasons why individuals are not in the labor force vary widely.
In the CPS and ASEC data, the respondents were asked the main reason for not working. The reasons included: ill or disabled, retired, taking care of home or family, going to school, could not find work and other.
In 2023, a total of 93.6 million individuals aged 16 and older neither worked nor looked for work at any time during the year. Among this group, 48.6 million people reported retirement as their main reason for not working. Approximately 14.9 million individuals stated that they were attending school, while 14.7 million cited illness or disability as the main factor. Additionally, 12.7 million people indicated that taking care of home or family was the main reason for not working in 2023. Nearly 1.8 million individuals selected “other reasons,” and roughly 1.0 million cited “could not find work.”
Retirement is the main reason for not working for about half of the individuals not in the labor force in 2023. Among those aged 65 years and older, 91% of individuals in this group cited retirement as the main reason for not working. Overall, about 44% of individuals not in the labor force were due to the self-reported reason of retirement and aged 65 years and older. Individuals in this 44% share are unlikely to return to the labor force.
While an aging population is a major driver behind the growth of individuals not participating in the labor force, other reasons people give for not engaging in the workforce also play an important role.
For individuals aged 16 to 24, the majority cited going to school as the main reason not working in 2023. In other words, for those citing going to school, 87% were between the ages of 16 and 24. Overall, about 14% of the not-in-labor-force population was due to the self-reported reason of going to school and aged 16 to 24. This group is likely to enter the labor force after graduation, although younger individuals will likely replace them in education settings.
Prime-age workers, aged 25 to 54, historically represent a larger share of the labor force compared to other age groups. However, men and women in this age group have different reasons for not working in 2023. More than half of women (62%) reported taking care of home or family as the main reason for not working, while 48% of men cited illness or disability as their primary reason.
Among prime-age individuals, those with less education were more likely to be out of the labor force than their more educated counterparts. In 2023, 15% of prime-age men with a high school diploma or less were not in the labor force, compared to 10% of those with some college and 5% of those with a bachelor’s degree or higher. The trend was similar among prime-age women, with 33% of those with a high school diploma or less not in the labor force, compared to 20% of those with some college and 13% of those with a bachelor’s degree or more.
It is difficult to predict with certainty whether prime-age individuals currently not in the labor force will enter it. However, several factors could encourage individuals to enter or return to the labor market, including improved economic conditions, the availability of remote work, workplace policies, and retraining opportunities.
Last, based on the CPS and ASEC data, only a small proportion of the remaining population reported the main reasons for not working were that they could not find work and other reasons.
Conclusion
These numbers highlight both challenges and opportunities in expanding the labor force to support construction employment. According to the BLS’s monthly job report, approximately 6% of individuals currently not in the labor force and aged 16 to 64 could potentially be recruited into the workforce. Furthermore, the construction labor force is aging. The building industry must recruit the next generation of workers as industry activity grows in the years ahead, given the growth in population not in the labor force.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .