Total outstanding U.S. consumer credit stood at $5.15 trillion for the fourth quarter of 2024, increasing at an annualized rate of 4.22% (seasonally adjusted), according to the Federal Reserve’s G.19 Consumer Credit Report. This is an uptick from the third quarter of 2024’s rate of 2.47%.
The G.19 report excludes mortgage loans, so the data primarily reflects consumer credit in the form of student loans, auto loans, and credit card plans. As consumer spending has outpaced personal income, savings rates have been declining, and consumer credit has increased. Previously, consumer credit growth had slowed, as high inflation and rising interest rates led people to reduce their borrowing. However, in the last two quarters, growth rates have increased, reflecting the rate cuts that took place at the end of the third quarter.
Nonrevolving Credit
Nonrevolving credit, largely driven by student and auto loans, reached $3.76 trillion (SA) in the fourth quarter of 2024, marking a 3.11% increase at a seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR). This is an uptick from last quarter’s rate of 2.28%, and the highest in two years.
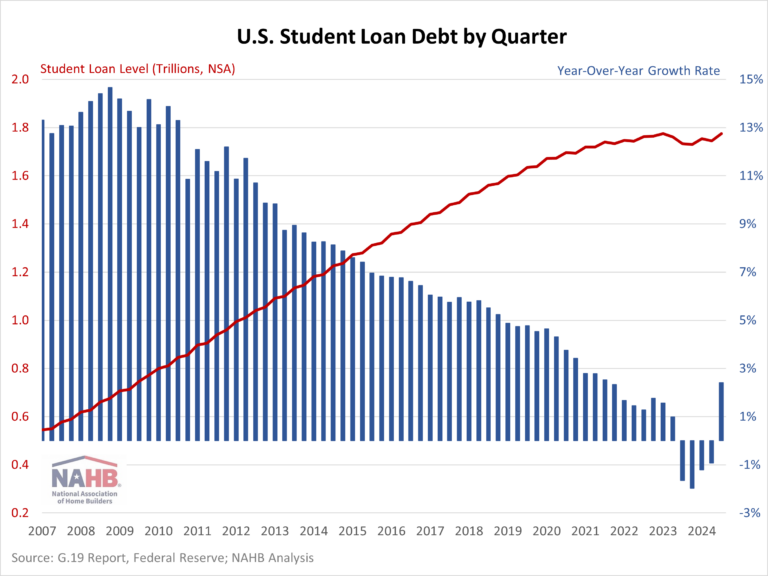
Student loan debt balances stood at $1.78 trillion (NSA) for the fourth quarter of 2024. Year-over-year, student loan debt rose 2.77%, the largest yearly increase since the second quarter of 2021. This shift partially reflects the expiration of the COVID-19 Emergency Relief for student loans’ 0-interest payment pause that ended September 1, 2023.
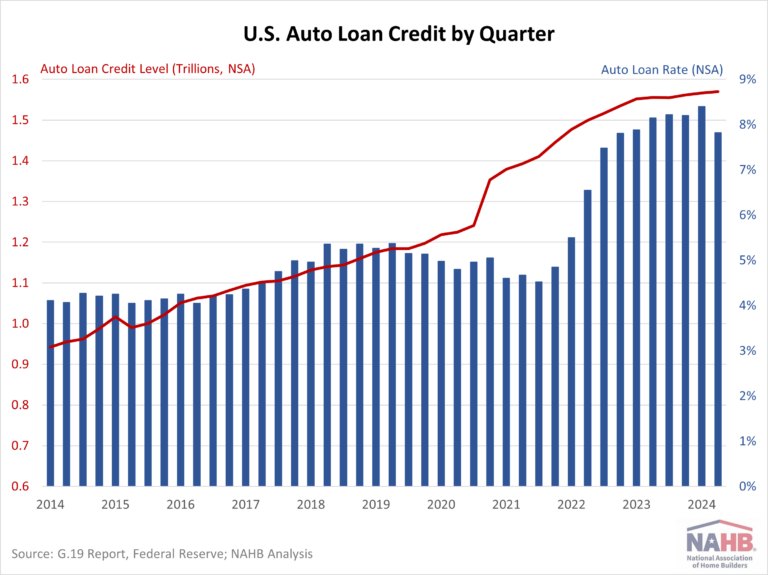
Auto loans reached a total of $1.57 trillion, showing a year-over-year increase of only 0.93%. This marks the second slowest growth rate since 2010, slightly above last quarter’s rate of 0.91%. The deceleration in growth can be attributed to several factors, including stricter lending standards, elevated interest rates, and overall inflation. Although interest rates for 5-year new car loans fell to 7.82% in the fourth quarter from a high of 8.40% in the third quarter, they remain at their highest levels in over a decade.
Revolving Credit
Revolving credit, primarily credit card debt, reached $1.38 trillion (SA) in the fourth quarter, rising at an annualized rate of 7.34%. This marked a significant increase from the third quarter’s 3.01% rate but was notably down from the peak growth rate of 17.58% seen in the first quarter of 2022. The surge in credit card balances in early 2022 was accompanied by an increase in the credit card rate which climbed by 4.51 percentage points over 2022. This was an exceptionally steep increase, as no other year in the past two decades had seen a rate jump of more than two percentage points.
Comparatively, so far in 2024 the credit card rate decreased 0.12 percentage points. For the fourth quarter of 2024, the average credit card rate held by commercial banks (NSA) was 21.47%.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .