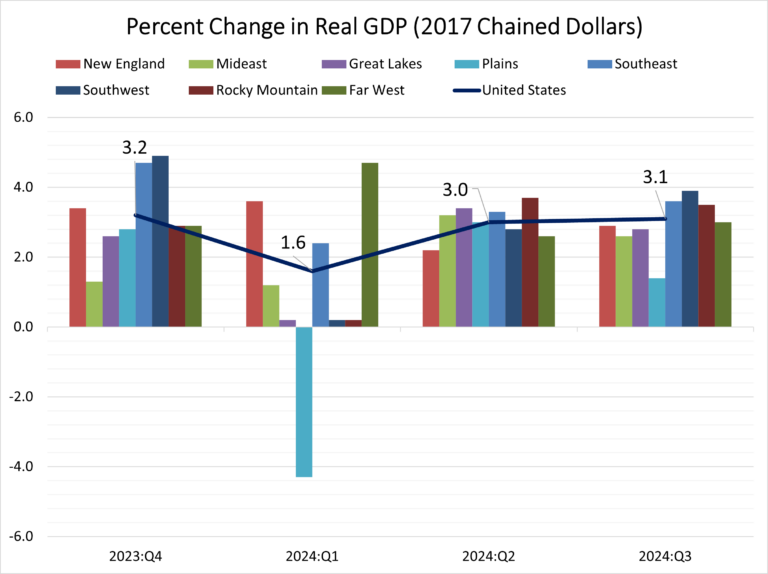
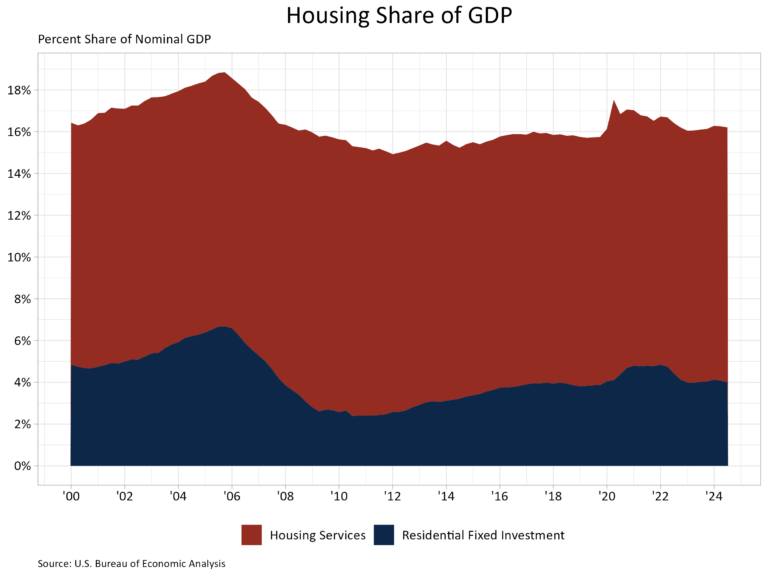
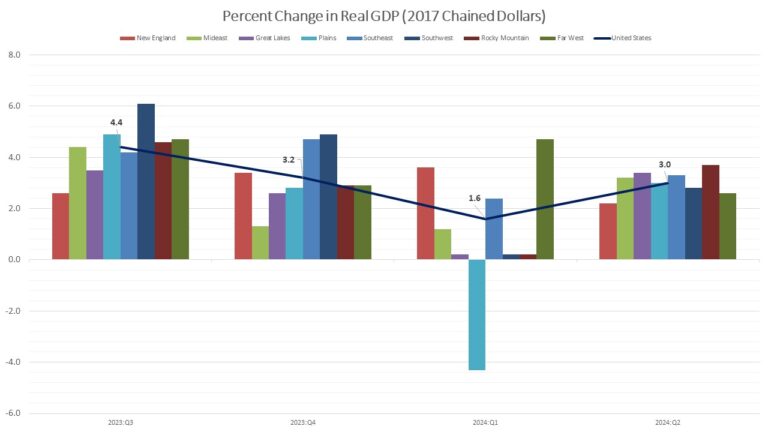
Real GDP of metropolitan areas rose 2.7% in 2023, with the “real estate, rental and leasing” sector contributing 0.34 percentage points and construction contracting growth by 0.11 percentage points. While many metro areas followed the national growth trend, each region has its unique economic narrative. This article explores the economic trends driving these outcomes, focusing on the leading metro areas in real GDP growth, the construction sector’s standout performers over a five-year period, and the top MSAs benefiting from growth in real estate, rental, and leasing.
In 2023, real GDP increased in 348 Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSAs), decreased in 34 MSAs, and remained unchanged in 3 MSAs, according to the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA). The data, which was recently released in December 2024, shows the range of growth spanned from 42.9% in Midland, TX, to a contraction of -9.3% in Elkhart-Goshen, IN. Three MSAs—Ithaca, NY, Joplin, MO, and Longview, WA—saw no change in real GDP.
The oil and gas sector played a significant role in driving growth in many MSAs. Midland, TX, recorded the highest growth due to a surge in oil production, with the “mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction” industry contributing a hefty 41.2 percentage points to the metro area’s GDP growth. Furthermore, among the top five highest growth areas, four had this industry as the leading contributor.
Top Five MSAs by Real GDP Growth and Leading Contributing Industry
Metro Area2023 Real GDP Growth (%)Largest Contributing IndustryContribution (Percentage Points)Midland, TX42.9Mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction41.2Greeley, CO18.5Mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction15.5El Centro, CA16.4Agriculture, forestry, fishing, and hunting14.4Odessa, TX11.6Mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction7.1Wheeling, WV-OH10.7Mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction9.9
Construction Sector Growth (2018–2023)
From 2018 to 2023, the construction industry exhibited a mixed performance, with 140 MSAs reporting positive compound annual growth rates (CAGR), 188 recording declines, and 5 showing no change. States like Idaho, Arizona, and Florida emerged as hotspots for construction growth during this period while states in the East North Central division appear to have slowdowns in this sector.
Elizabethtown-Fort Knox, KY, led with a 14.4% CAGR in construction. This boom was primarily driven by the development of the BlueOval SK Battery Park, slated to begin production in 2025. This joint venture between Ford Motor Company and SK On, a South Korean electric vehicle (EV) supplier, is expected to be the largest EV battery manufacturing facility globally.
According to a study by the Hardin County Chamber of Commerce (HCCC), the project is estimated to:
Generate $1.6 billion in construction payroll.
Create 5,000 jobs by the end of 2025.
Require 3,100 additional housing units to accommodate new workers.
Top Five MSAs for Construction Growth (2018–2023):
Metro AreaCAGR (%)Average Contribution (Percentage Points)Elizabethtown-Fort Knox, KY14.40.45Clarksville, TN-KY10.80.03Punta Gorda, FL10.61.12Jacksonville, NC10.20.32The Villages, FL10.11.23
Real Estate, Rental, and Leasing Growth (2018–2023)
The real estate, rental, and leasing sector also showed robust growth in many regions, with 209 MSAs experiencing positive growth during the five-year period. The Villages, FL, recorded the highest CAGR at 14.1%, reflecting its status as the nation’s largest community designed for an aging population.
Other MSAs like Jonesboro, AR, saw significant real estate growth due to proximity to Arkansas State University, while Austin-Round Rock-Georgetown, TX, benefited from a population influx because of its thriving tech economy.
Top Five MSAs for Real Estate Growth (2018–2023):
Metro AreaCAGR (%)Average Contribution (Percentage Points)The Villages, FL14.13.6Jonesboro, AR12.11.2Twin Falls, ID10.81.1Austin-Round Rock-Georgetown, TX10.71.4El Centro, CA10.60.6
Visit NAHB’s dashboard for additional data and visualizations on demographics, housing market and the economy for all metro areas.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .