The continued shortage of existing homes for sale has helped to keep new single-family construction growing across all regions, according to the latest National Association of Home Builders release of the Home Building Geography Index (HBGI). Despite persistent factors that continue to affect housing affordability, including a limited supply of buildable lots, rising construction costs, and a shortage of skilled labor, single-family construction grew over all four quarters of 2024. Multifamily construction remained lackluster but did feature some growth in lower density areas.
Single-Family
All HBGI-tracked geographies posted another quarter of growth in the fourth quarter after peaking in the second quarter. The HBGI is constructed using permit data, which has continued to post higher volumes than last year despite residential construction dealing with persistent structural issues.
Among the HBGI geographies, the highest growth in the fourth quarter of 2024 was registered in small metro core counties, which increased 10.3% year-over-year on a four-quarter moving average basis (4QMA). The market with the lowest level of growth was non metro/micro counties which were up 4.8% year-over-year (4QMA).
In terms of market share, single-family construction took place primarily in small metro core county areas, representing 29.1% of single-family construction. The smallest single-family construction market remained non metro/micro county areas, with a 4.2% market share.
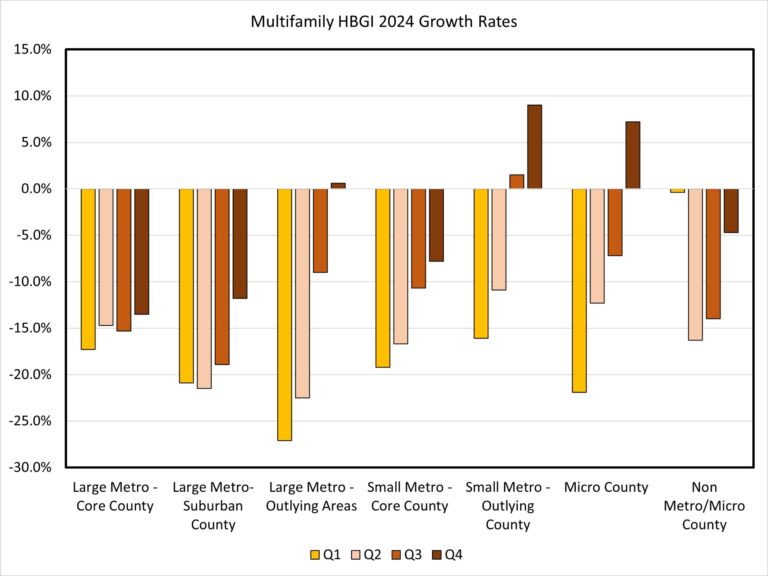
Multifamily
Multifamily construction continued to register negative growth rates across the largest markets, with large metro core county areas posting a decline of 13.5% quartering in the fourth quarter (4QMA). While permit levels remain lower for new multifamily construction, there were some positive signs in less densely populated areas. Small metro outlying county areas had the largest growth rate in the fourth quarter at 9.0%, the second consecutive quarter of growth. These areas make up around 5.0% of the total multifamily construction market.
The fourth quarter of 2024 HBGI data along with an interactive HBGI map can be found at http://nahb.org/hbgi.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .