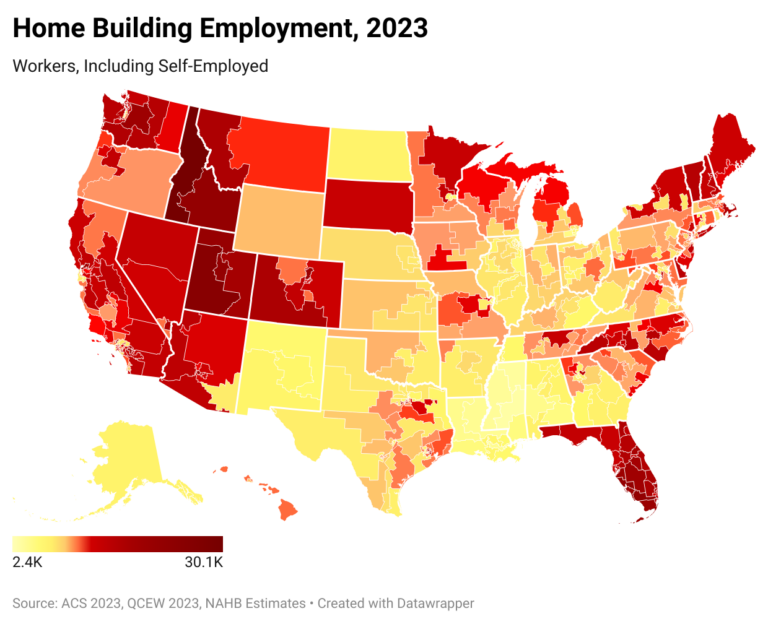
As the number of housing units under construction peaked in 2023, the industry set another record employing close to 11.4 million people, including self-employed workers. NAHB estimates that out of this total, 4.7 million people worked in residential construction, accounting for 2.9% of the U.S. employed civilian labor force. Home building in the Mountain Division, as well as in Vermont and Florida, stand out as generating a significantly higher share of local jobs, with residential construction generating more than 5% of all jobs in Idaho and Montana. NAHB’s analysis also identifies congressional districts where home building accounts for particularly high employment levels and share of local jobs.
Not surprisingly, the most populous state—California—also has the most residential construction workers. Over 640,000 California residents worked in home building in 2023, accounting for 3.4% of the state employed labor force.
Fast-growing Florida comes in second with 468,000 residential construction workers. The state stands out for registering one of the fastest growing populations since the start of the pandemic, which undoubtedly boosted housing and construction workforce demand. Florida’s large stock of vacation and seasonal housing further boosts demand for residential construction workers. As a result, in Florida, residential construction workers account for a relatively high 4.4% of the employed labor. Even though this share is well above the national average (2.9%), it is significantly lower than in 2006, when Florida registered the highest share among all 50 states and the District of Columbia, at 6.5%.
Similar to Florida, fast-growing states with a high prevalence of seasonal, vacation homes top the list of states with the highest share of residential construction workers in 2023. Three states in the Mountain Division – Idaho, Montana, and Utah – take the top spots on the list with 5.5%, 5.1% and 4.9% of the employed labor force working in home building. Vermont is next on the list with a share of 4.6%.
As of 2023, the average congressional district has about 10,800 residents working in residential construction, but that number is often significantly higher. In Idaho’s 1st Congressional District, over 30,000 residents are in home building and Utah’s 2nd Congressional District has over 25,000 residents working in home building.
Eight other congressional districts have over 20,000 residents working in residential construction – Florida’s 26th, Utah’s 4th, Idaho’s 2nd, Florida’s 17th, Arizona’s 3rd, Utah’s 1st, Florida’s 28th, and California’s 29th.
By design, Congressional districts are drawn to represent roughly the same number of people. So generally, large numbers of residential construction (RC) workers translate into high shares of RC workers in their district employed labor forces. Idaho’s 1st tops this list as well, registering the highest share of residential construction workers in the employed labor force, 6.4%. Florida’s 17th is a close second with 6.3% of the district labor force employed in home building. Next on the list are two Mountain division districts – Montana’s 1st and Utah’s 2nd – with shares of 5.8%, followed by two Florida’s districts – 19th (5.7%) and 26th (5.6%). California’s 29th (5.4%) and 39th (5.3%) also register shares far exceeding the national average of 2.9%.
At the other end of the spectrum there are several districts that contain parts of large urban areas: the District of Columbia, the 12th of New York, located in New York City, Pennsylvania’s 3rd that includes areas of the city of Philadelphia, Georgia’s 5th that includes most of Atlanta, and among others, Illinois’s 7th and 9th, covering parts of Chicago. Most residents in these urban districts tend to work in professional, scientific, and technical services. The District of Columbia stands out for having the lowest number of RC workers, with just 1,400 residing in the district. At the same time, it has a disproportionally large share of public administration workers. The 12th District of New York and the 7th District of Illinois are home to a very large group of finance and insurance workers. Meanwhile, in Pennsylvania’s 2nd, more than a third of residents work in health care and educational services.
The NAHB residential construction employment estimates include self-employed workers. Counting self-employed is particularly important in the home building industry since they traditionally make up a larger share of the labor force than in the U.S. total workforce.
The new NAHB home building employment estimates only include workers directly employed by the industry and do not count jobs created in related industries– such as design and architecture, furniture making, building materials, landscaping, etc. As a result, the estimates underestimate the overall impact of home building on local employment.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .