Real gross domestic product (GDP) increased in 45 states and the District of Columbia in the third quarter of 2024 compared to the second quarter of 2024 according to the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA). Iowa reported no change during this time. The percent change in real GDP ranged from a 6.9 percent increase at an annual rate in Arkansas to a 2.3 percent decline in North Dakota.
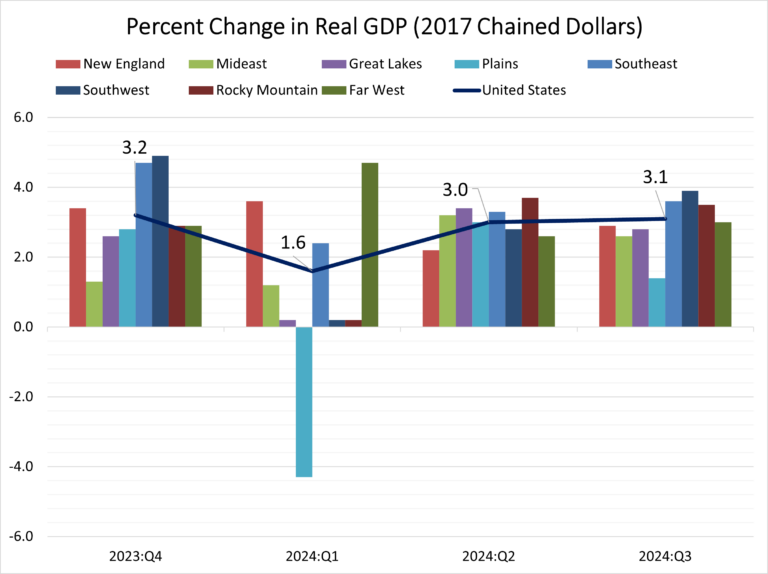
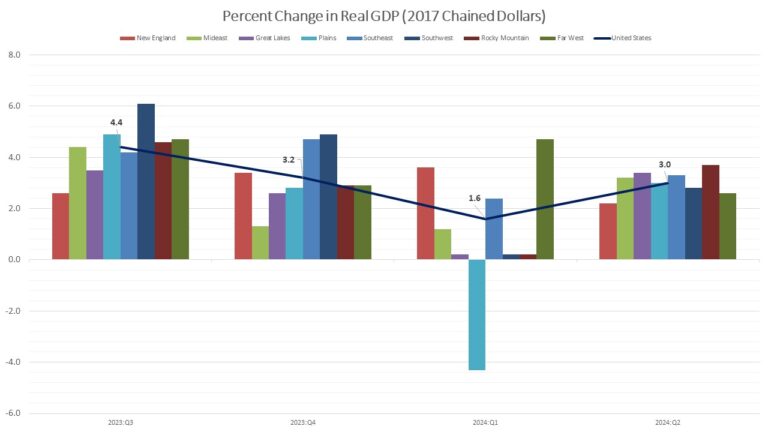
Nationwide, growth in real GDP (measured on a seasonally adjusted annual rate basis) increased 3.1 percent in the third quarter of 2024, which is roughly the same as the second quarter level of 3.0 percent. Retail trade, health care and social assistance, and information were the leading contributors to the increase in real GDP across the country.
Regionally, real GDP growth increased in all eight regions between the second and the third quarter. The percent change in real GDP ranged from a 3.9 percent increase in the Southwest region (Arizona, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Texas) to a 1.4 percent increase in the Plains region (Iowa, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, and South Dakota).
At the state level, Arkansas posted the highest GDP growth rate (6.9 percent) followed by Alabama (6.0 percent) and Mississippi (5.1 percent). On the other hand, three out of the seven states that makes up and Plains region, South Dakota (-0.8 percent), Nebraska (-1.4 percent), and North Dakota (-2.3 percent) along with Montana (-0.1 percent) posted an economic contraction in the third quarter of 2024.
The agriculture, forestry, fishing, and hunting industry increased in 25 states, was the leading contributor to growth in five states including Arkansas, Alabama, and Mississippi, the states with the largest increases in real GDP. In contrast, this industry was the leading offset to growth in 14 states including North Dakota, Nebraska, South Dakota, and Montana, the only states with declines in real GDP.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .