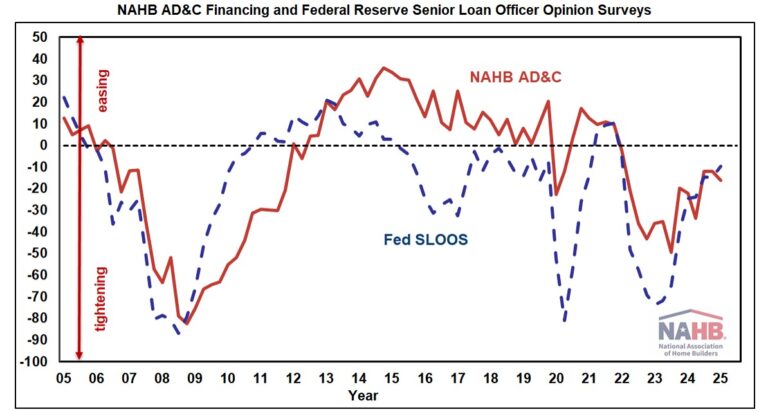
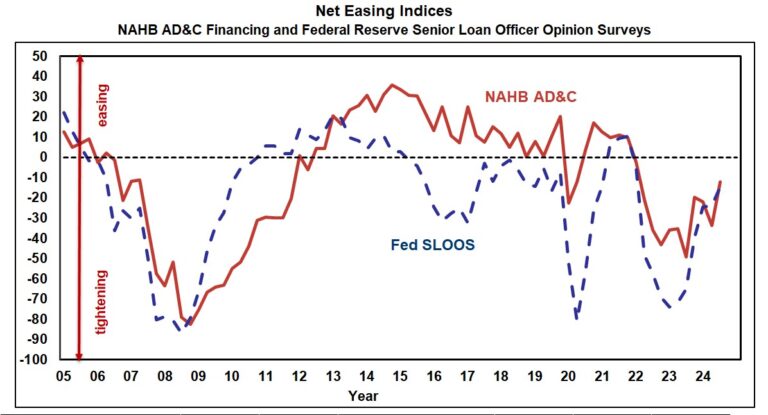
Borrowers and lenders agreed that credit for residential Land Acquisition, Development & Construction (AD&C) tightened further in the fourth quarter of 2024, according to NAHB’s survey on AD&C Financing and the Federal Reserve’s survey of senior loan officers. The net easing index derived from the NAHB survey posted a reading of -16.3, while the similar index derived from the Fed survey posted a reading of -9.5 (the negative numbers indicating that credit tightened since the previous quarter). Although the additional net tightening in the fourth quarter was modest (as indicated by negative numbers much closer to 0 than -100), this marks the twelfth consecutive quarter during which both surveys reported net tightening of credit for AD&C.
According to the NAHB survey, the most common ways in which lenders tightened in the fourth quarter were by lowering the loan-to-value or loan-to-cost ratio (reported by 72% of builders and developers) and reducing the amount they are willing to lend (61%). Additional information from the Fed’s survey of lenders—including measures of demand and net easing for residential mortgages—is discussed in an earlier post.
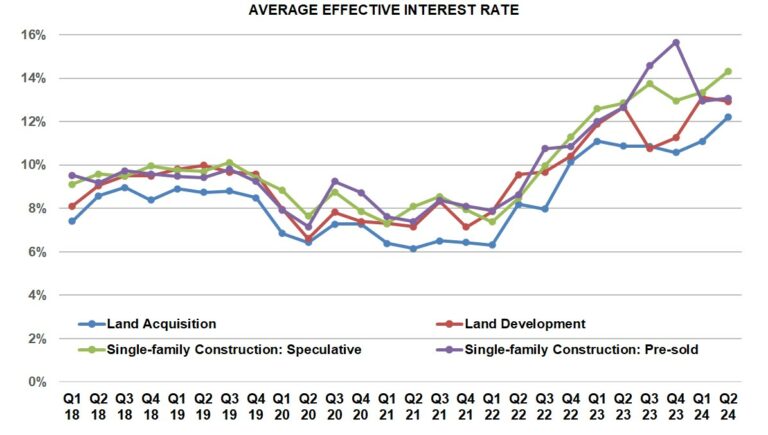
For the second consecutive quarter, the contract interest rate declined on all four categories of loans tracked in the NAHB AD&C survey. In the fourth quarter of 2024, the average contract interest rate declined from 8.50% in 2024 Q3 to 8.48% on loans for land acquisition, from 8.83% to 8.28% on loans for land development, from 8.54% to 8.34% on loans for speculative single-family construction, and from 8.11% to 7.75% on loans for pre-sold single-family construction.
In addition to the contract rate, initial points charged on the loans can be an important component of the overall cost of credit, especially for loans paid off as quickly as typical single-family construction loans. In the fourth quarter, trends on initial points were mixed. The average points declined on loans for land acquisition, from 0.77% in 2024 Q3 to 0.55%. However, average points increased quarter-over-quarter on loans for land development (from 0.68% to 0.75%), pre-sold single-family construction (from 0.26% to 0.67%) and speculative single-family construction (from 0.49% to 0.64%).
Not surprisingly, the conflicting trends described above resulted in mixed results for the overall cost of AD&C credit, as indicated by the average effective interest rate (which takes both the contract rate and initial points into account). In the fourth quarter of 2024, the average effective rate declined on loans for land acquisition from 11.17% in 2024 Q3 to 10.79%, and on loans on land development from 12.82% to 12.12%. Meanwhile, the average effective rate increased on loans for speculative single-family construction from 12.61% to 12.86%, and on loans for pre-sold single-family construction from 12.03% to 12.98%. Even after these disparate changes between 2024 Q3 and 2024 Q4, the average effective interest rates on all four categories of AD&C loans were at least slightly lower in 2024 Q4 than they were in 2024 Q2.
More detail on credit conditions for residential builders and developers is available on NAHB’s AD&C Financing Survey web page.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .