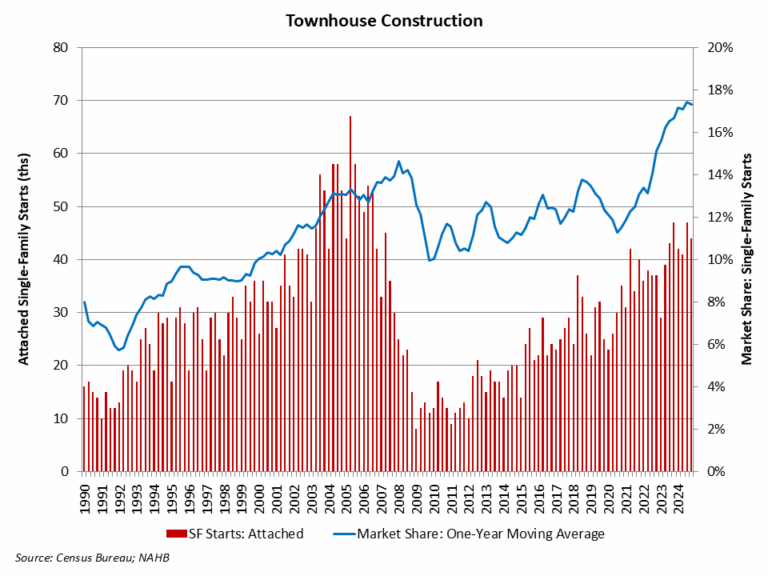
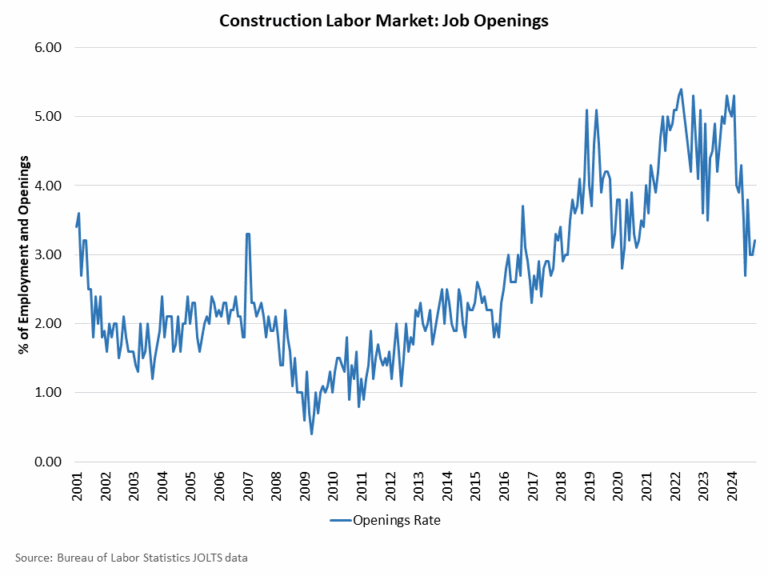
Townhouse construction expanded 10% during 2024, outpacing the rest of the single-family home building market.
According to NAHB analysis of the most recent Census data of Starts and Completions by Purpose and Design, during the fourth quarter of 2024, single-family attached starts totaled 44,000. Over the last four quarters (2024 as a whole), townhouse construction starts totaled a strong 174,000 homes, which is 10% higher than the prior four-quarter period (158,000 in 2023). Townhouses made up 19% of single-family housing starts for the fourth quarter of the year, a data series high.
Using a one-year moving average, the market share of newly-built townhouses stood at 17.3% of all single-family starts for the fourth quarter. With recent gains, the four-quarter moving average market share is near the highest on record, for data going back to 1985.
Prior to the current cycle, the peak market share of the last two decades for townhouse construction was set during the first quarter of 2008, when the percentage reached 14.6% on a one-year moving average basis. This high point was set after a fairly consistent increase in the share beginning in the early 1990s.
The long-run prospects for townhouse construction are positive given growing numbers of homebuyers looking for medium-density residential neighborhoods, such as urban villages that offer walkable environments and other amenities. Where it can be zoned, it can be built.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .