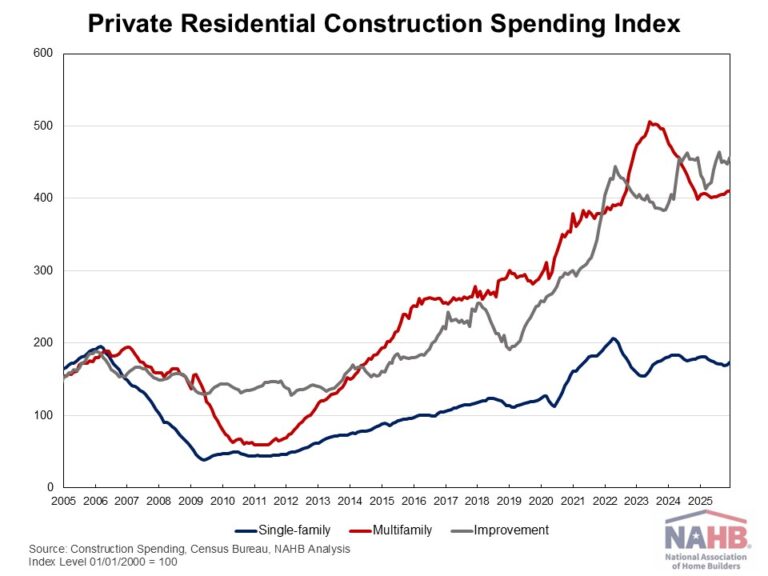
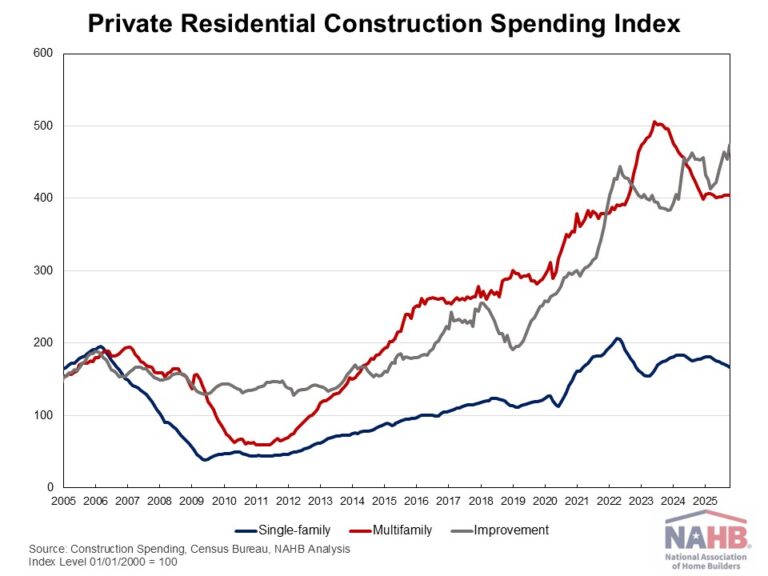
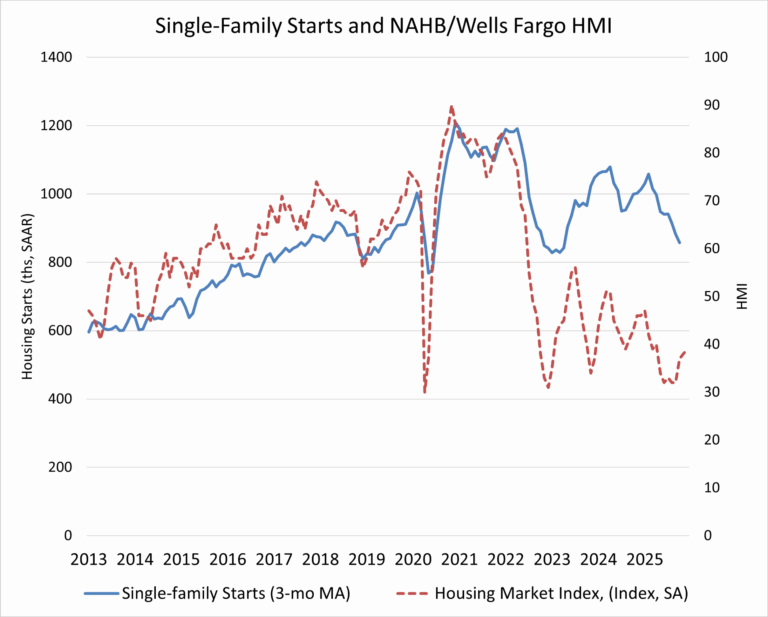Private residential construction spending was up 1.5% for the last month of 2025. This modest gain was driven primarily by increased spending on home improvements and single-family construction. Despite this increase, total spending remained 1.3% lower than a year ago, reflecting the continued impact of housing affordability challenges facing the sector.
According to the latest construction spending data from the U.S. Census, single-family construction spending was up by 1.6% in December, consistent with the soft builder confidence reflected in the NAHB/Wells Fargo Housing Market Index (HMI). Compared to a year ago, single-family construction spending decreased 3.6%. Meanwhile, multifamily construction spending edged up 0.1% in December, marking a seventh consecutive month of modest gains. Compared to a year earlier, multifamily spending was 2.9% higher. Improvement spending (remodeling) rose 1.8% for the month but stayed flat relative to a year ago.
The NAHB construction spending index is shown in the graph below. The index illustrates how spending on single-family construction has slowed since early 2024 under the pressure of elevated interest rates and concerns over building material tariffs. Multifamily construction spending growth has also slowed down after the peak in July 2023, with the index largely plateauing since late 2024. In contrast, improvement spending has been on an upward trend since the beginning of 2025.
Spending on private nonresidential construction was down 1.8% over a year ago. The annual private nonresidential spending decrease was primarily driven by a $26 billion drop in manufacturing construction spending, followed by a $2 billion decrease in healthcare construction spending.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .