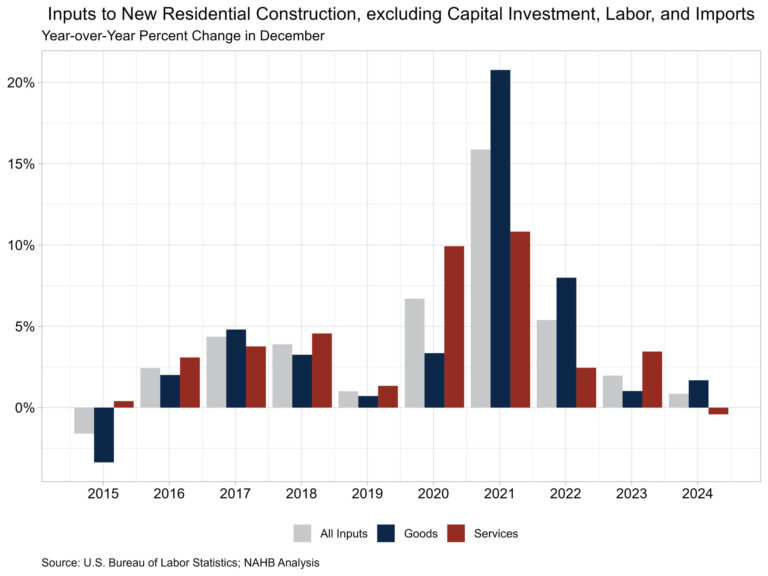
Prices for inputs to new residential construction—excluding capital investment, labor, and imports—were unchanged in December according to the most recent Producer Price Index (PPI) report published by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. This index grew 0.8% over 2024, the lowest yearly increase in the index since its inception in 2014.
The inputs to the new residential construction price index can be broken into two components—one for goods and another for services. The goods component increased 1.7% over the year, while services decreased 0.4%. For comparison, the total final demand index increased 3.3% in 2024, with final demand with respect to goods up 1.8% and final demand for services up 4.0% over the year.
Input Goods
The goods component has a larger importance to the total residential construction inputs price index, representing around 60%. The price of input goods to new residential construction was down 0.1% in December from November. The input goods to residential construction index can be further broken down into two separate components, one measuring energy inputs with the other measuring goods less energy inputs. The latter of these two components simply represents building materials used in residential construction, which makes up around 93% of the goods index.
The price of goods used in residential construction grew 1.7% in 2024, slightly higher than the growth in 2023 of 1.0%. This growth can be attributed to the rise in the prices of building materials, which grew 2.2% in 2024. The price of energy inputs fell for the second straight year, down 5.3% in 2024.
At the individual commodity level, the five commodities with the highest importance for building materials to the new residential construction index were as follows: ready-mix concrete, general millwork, paving mixtures/blocks, sheet metal products, and wood office furniture/store fixtures. Across these commodities, there was price growth for most commodities in 2024 except for sheet metal products. Ready-mix concrete was up 5.1%, wood office furniture/store fixtures up 4.3%, general millwork up 2.5%, paving mixtures/blocks up 2.3% while sheet metal products were down 0.2%. The commodity used in new residential construction the featured the highest price growth in 2024 was softwood lumber, not edge worked, which increased 14.7% in 2024. The commodity where prices declined the most was No. 2 diesel fuel, down 13.9%.
Input Services
Prices of inputs to residential construction for services were up 0.5% in December from November. The price index for service inputs to residential construction can be broken out into three separate components: a trade services component, a transportation and warehousing services component, and a services excluding trade, transportation and warehousing component. The most significant component is trade services (around 60%), followed by services less trade, transportation and warehousing (around 29%), and finally transportation and warehousing services (around 11%). The largest component, trade services, was down 1.8% in 2024 after growing 5.8% in 2023. Across individual services, credit deposit services advanced the most in 2024, up 21.2% over the year while the prices for metal, mineral and ore wholesaling services fell the most, down 19.2%.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .